心理實驗法第六講:Basic of control
出自KMU Wiki
(修訂版本間差異)
| 在2012年12月1日 (六) 16:34所做的修訂版本 (編輯) Mi (對話 | 貢獻) (→心理學實驗中另一項問題) ←上一個 |
當前修訂版本 (2019年10月30日 (三) 23:52) (編輯) (撤銷) U105020054 (對話 | 貢獻) (→Within-subject) |
||
| (13個中途的修訂版本沒有顯示。) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| - | Basic of Control and Factorial Design<br> | + | Basic of Control and Factorial Design<br>心理實驗法一百零一學年度第五講<br>前面幾張省略(因為與上一講重復) |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | == Placebo == | ||
| - | * Case Study | + | == Case Study 1 == |
| + | |||
| + | * 靈異觀點 | ||
| + | ** 不知同學們多少相信靈異事件? | ||
| + | ** 靈異故事先天讓人相信? | ||
| + | ** 是先給於暗示有效? | ||
| + | ** 還是後給於解釋有效? | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | * 王震武與林文瑛(2005) | ||
| + | ** IV 預測、解釋、控制 | ||
| + | ** DV 靈異觀點接受度 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | * Case Study 1 cont. | ||
| + | ** 二十二歲的陳小姐一向體弱多病。 | ||
| + | <br> 不久前,她到某山區去探望一位長輩,回來就病倒了。她的症狀是,時常發燒,臉色蒼白,睡覺時囈語連連。 經過徹底檢查之後,醫生也找不出明顯的病因。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | * Case Study 1 cont. 2 | ||
| + | ** 操弄 | ||
| + | *** 預測(暗示)在文章之前加,例如: | ||
| + | **** 曾有一位法師說,她的陰氣較重,容易遇到「不乾淨的東西」,因此身體狀況較差。 | ||
| + | *** 解釋(事後)在文章之後加,例如: | ||
| + | **** 朋友們帶她去某寺廟拜拜,該廟的法師 說,陳小姐的陰氣較重,容易遇到「不乾淨的東西」,這趟山區之行正好讓她遇上了,所以才會生病。 | ||
| + | *** 控制組,只有案例 | ||
| + | ** 結果 | ||
| + | *** 預測、解釋均比控制組更相信靈異,但預測與解釋間沒有差異 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | * Case Study 1 cont. 3 | ||
| + | ** 控制組的作用 | ||
| + | *** 如果沒有控制組 | ||
| + | *** 預測與解釋一樣 | ||
| + | **** 那學生到底信不信靈異觀點?? | ||
| + | ** Control group的作用 | ||
| + | *** 顯示自然狀態 | ||
| + | *** 基準線(base line) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Control == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 是心理學實驗(以及各種研究)中最重要的議題 | ||
| + | * 也是最難處理的問題 | ||
| + | * 也最容易出問題的地方 | ||
| + | * 所以 以後會重復這個地方 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Case Study 2 == | ||
| + | |||
| * Paul (1966) speech phobia的治療 | * Paul (1966) speech phobia的治療 | ||
| * 分四組(共67人) | * 分四組(共67人) | ||
| 第33行: | 第79行: | ||
| *** 韓國裁判? | *** 韓國裁判? | ||
| ** 如何避免? | ** 如何避免? | ||
| - | * Blind control | + | ** Blind control |
| ** Single blind | ** Single blind | ||
| ** Double blind | ** Double blind | ||
| - | * Case Study | + | |
| + | * Case Study 3 | ||
| * Rosenthal and Fode (1963) | * Rosenthal and Fode (1963) | ||
| ** 告知學生 | ** 告知學生 | ||
| 第44行: | 第91行: | ||
| *** Maze-bright的老鼠表現遠較maze-dull為佳 | *** Maze-bright的老鼠表現遠較maze-dull為佳 | ||
| *** 其實兩組老鼠由同一種老鼠中隨機抽取 | *** 其實兩組老鼠由同一種老鼠中隨機抽取 | ||
| + | |||
| == Within-subject == | == Within-subject == | ||
| - | * Between-subject design | + | * Between-subject design |
| - | ** Group A Experimental | + | ** Group A Experimental condition Measure |
| ** Group B Control condition Measure | ** Group B Control condition Measure | ||
| - | * Within-subject design | + | * Within-subject design |
| ** Subject A->experimental condition1 + experimental condition2 +...... | ** Subject A->experimental condition1 + experimental condition2 +...... | ||
| - | + | == Within的好處 == | |
| * 減少subject數量 | * 減少subject數量 | ||
| 第59行: | 第107行: | ||
| * 較易顯著(統計上) | * 較易顯著(統計上) | ||
| - | === Why易顯著 === | ||
| - | '''由SS(sum of square)看''' | ||
| - | * SSt=SSb+SSw (between subject) | ||
| - | 其中SSt代表Sum of Square total,是整體的變異大小。SSb代表Sum of Square between groups,也就是組間的變異大小。SSw代表Sum of Square within groups,是組內的變異大小。統計顯著性考驗時,則先各求MSb(Mean Square between groups)與MSw(Mean Square within groups)再求其比值(就是F值)。 | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | + | == Case Study 4 == | |
| - | + | [[Image:5-1.gif]] | |
| - | + | * 杜韋莉與櫻井(2009) | |
| - | + | ** 單眼可見遮蔽線索對於雙眼立體視覺的影響 | |
| - | * | + | ** 材料:錯覺輪廓 |
| - | + | ** 呈現方式:雙眼分離呈現 (dichoptic presentation) | |
| - | * | + | ** 關鍵想法及概念 |
| - | + | *** 雙眼立體視覺 | |
| + | **** 雙眼像差(binocular disparity) | ||
| + | *** 單眼立體線索 | ||
| + | **** 圖畫線索(pictorial cues) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Case Study 4 cont. | ||
| + | ** 實驗設計 | ||
| + | *** 2 X 2 X 2 完全受試者內多因子設計(多因子設計是什麼下一次再說) | ||
| + | *** 獨變項:有無單眼可見遮蔽線索、圖形類別、像差(正負) | ||
| + | *** 依變項:實驗參與者判斷錯覺輪廓上浮或下沉 | ||
| + | *** 步驟:注意符號後以完全隨機的順序出現8種條的任一種畫面,實驗參與者判斷換下一個嘗試(trail) | ||
| + | *** 每一個條件出現三次,故共有24個嘗試 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Case Study 4 cont.2 | ||
| + | ** 總覽 | ||
| + | [[Image:5-2.png]] | ||
| + | == Trial == | ||
| + | [[Image:5-3.PNG]] | ||
| + | * 嘗試 | ||
| + | ** 心理實驗中基本單位 | ||
| + | ** 在實驗心理學中常以一連串畫面呈現 | ||
| + | == Why易顯著 == | ||
| - | + | * 由SS(sum of square)看 | |
| + | ** SSt=SSb+SSw | ||
| + | ** SSt=SSb.sub+SSw.sub=SSb.sub+SStreatment+SSresidual | ||
| + | * 由個別來看 | ||
| + | ** xij=μ+βj+εij | ||
| + | ** xij=μ+βj+πi+εij | ||
| + | ** βj為treatment | ||
| + | ** πi為individual difference | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == 不能用within的時機 == | ||
| * 以下時不可用(較不適用)within-subject design | * 以下時不可用(較不適用)within-subject design | ||
| 第84行: | 第156行: | ||
| ** 呈現的次序會影響結果時 | ** 呈現的次序會影響結果時 | ||
| ** 有以上嫌疑時 | ** 有以上嫌疑時 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == 心理實驗與儀器 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 呈現刺激、記錄反應 | ||
| + | ** 使用儀器 | ||
| + | *** 精準 | ||
| + | *** 較不會有experimenter bias | ||
| + | ** 也可以呈現、收集一般無法查覺的刺激與反應 | ||
| + | *** 時間:以毫秒計 | ||
| + | *** 強度:接近閾限 | ||
| + | * 早在十九世紀Wundt就設計了! | ||
| + | ** 台大心理系所藏古典儀器 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Case Study 5 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 葉重新與劉英茂(1972)檢驗辨識漢字時可能影響的因素 | ||
| + | ** 測量漢字的辨識閾(recognition threshold) | ||
| + | * 實驗操弄漢字的意義度、筆劃及對稱性 | ||
| + | * 實驗利用吉氏速示器(Gerbrands tachistoscope) | ||
| + | * 程序:極限法(limit method) | ||
| + | * 結果:意義度愈高,筆畫愈少的漢字辨識閾愈低 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 速示器(tachistoscope) | ||
| + | ** 快速呈現刺激 | ||
| + | [[Image:5-4.PNG]] | ||
| == PC與Psychology == | == PC與Psychology == | ||
| 第108行: | 第206行: | ||
| * Control of IV | * Control of IV | ||
| ** Spallazani實驗中精液的不同 | ** Spallazani實驗中精液的不同 | ||
| - | ** 人工環境中金絲雀築巢 | ||
| * Control environment | * Control environment | ||
| ** 實驗組與控制組間的差異除了上面控制以外控制成相當 | ** 實驗組與控制組間的差異除了上面控制以外控制成相當 | ||
| 第116行: | 第213行: | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | [[心理實驗法| 回心理實驗法目錄頁]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
當前修訂版本
Basic of Control and Factorial Design
心理實驗法一百零一學年度第五講
前面幾張省略(因為與上一講重復)
目錄 |
[編輯] Case Study 1
- 靈異觀點
- 不知同學們多少相信靈異事件?
- 靈異故事先天讓人相信?
- 是先給於暗示有效?
- 還是後給於解釋有效?
- 王震武與林文瑛(2005)
- IV 預測、解釋、控制
- DV 靈異觀點接受度
- Case Study 1 cont.
- 二十二歲的陳小姐一向體弱多病。
不久前,她到某山區去探望一位長輩,回來就病倒了。她的症狀是,時常發燒,臉色蒼白,睡覺時囈語連連。 經過徹底檢查之後,醫生也找不出明顯的病因。
- Case Study 1 cont. 2
- 操弄
- 預測(暗示)在文章之前加,例如:
- 曾有一位法師說,她的陰氣較重,容易遇到「不乾淨的東西」,因此身體狀況較差。
- 解釋(事後)在文章之後加,例如:
- 朋友們帶她去某寺廟拜拜,該廟的法師 說,陳小姐的陰氣較重,容易遇到「不乾淨的東西」,這趟山區之行正好讓她遇上了,所以才會生病。
- 控制組,只有案例
- 預測(暗示)在文章之前加,例如:
- 結果
- 預測、解釋均比控制組更相信靈異,但預測與解釋間沒有差異
- 操弄
- Case Study 1 cont. 3
- 控制組的作用
- 如果沒有控制組
- 預測與解釋一樣
- 那學生到底信不信靈異觀點??
- Control group的作用
- 顯示自然狀態
- 基準線(base line)
- 控制組的作用
[編輯] Control
- 是心理學實驗(以及各種研究)中最重要的議題
- 也是最難處理的問題
- 也最容易出問題的地方
- 所以 以後會重復這個地方
[編輯] Case Study 2
- Paul (1966) speech phobia的治療
- 分四組(共67人)
- 接受behavior therapy(15人)
- 接受insight therapy(15人)
- 吃無害也無效的藥丸(15人)
- 未接受任何治療(control 22人)
- DV
- 四位clinical psychologist(不知情)之前後測差異
- 結果
- Behavior 進步 100%
- Insight 進步 60%
- Pills 進步 73%
- Control 進步 32%
- 第三組稱為
- Placebo control group
- 所吃的藥稱為
- Placebo pills
- 所呈現的效果為
- Placebo effects
- Experimenter Bias
- 前面的實驗
- 如果打分者知道所評分對象接受了什麼治療...
- Scorer's bias
- 韓國裁判?
- 如何避免?
- Blind control
- Single blind
- Double blind
- 前面的實驗
- Case Study 3
- Rosenthal and Fode (1963)
- 告知學生
- 一組老鼠為maze-bright
- 另一組老鼠為maze-dull
- 結果
- Maze-bright的老鼠表現遠較maze-dull為佳
- 其實兩組老鼠由同一種老鼠中隨機抽取
- 告知學生
[編輯] Within-subject
- Between-subject design
- Group A Experimental condition Measure
- Group B Control condition Measure
- Within-subject design
- Subject A->experimental condition1 + experimental condition2 +......
[編輯] Within的好處
- 減少subject數量
- 可以不必考慮實驗組與控制組之環境是否相同
- 較易顯著(統計上)
[編輯] Case Study 4
- 杜韋莉與櫻井(2009)
- 單眼可見遮蔽線索對於雙眼立體視覺的影響
- 材料:錯覺輪廓
- 呈現方式:雙眼分離呈現 (dichoptic presentation)
- 關鍵想法及概念
- 雙眼立體視覺
- 雙眼像差(binocular disparity)
- 單眼立體線索
- 圖畫線索(pictorial cues)
- 雙眼立體視覺
- Case Study 4 cont.
- 實驗設計
- 2 X 2 X 2 完全受試者內多因子設計(多因子設計是什麼下一次再說)
- 獨變項:有無單眼可見遮蔽線索、圖形類別、像差(正負)
- 依變項:實驗參與者判斷錯覺輪廓上浮或下沉
- 步驟:注意符號後以完全隨機的順序出現8種條的任一種畫面,實驗參與者判斷換下一個嘗試(trail)
- 每一個條件出現三次,故共有24個嘗試
- 實驗設計
- Case Study 4 cont.2
- 總覽
[編輯] Trial
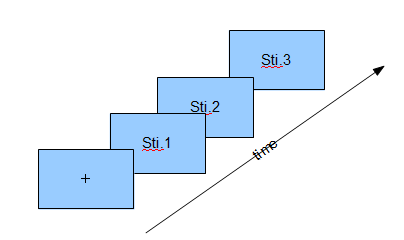
- 嘗試
- 心理實驗中基本單位
- 在實驗心理學中常以一連串畫面呈現
[編輯] Why易顯著
- 由SS(sum of square)看
- SSt=SSb+SSw
- SSt=SSb.sub+SSw.sub=SSb.sub+SStreatment+SSresidual
- 由個別來看
- xij=μ+βj+εij
- xij=μ+βj+πi+εij
- βj為treatment
- πi為individual difference
[編輯] 不能用within的時機
- 以下時不可用(較不適用)within-subject design
- 對受試者影響具持續性
- 呈現的次序會影響結果時
- 有以上嫌疑時
[編輯] 心理實驗與儀器
- 呈現刺激、記錄反應
- 使用儀器
- 精準
- 較不會有experimenter bias
- 也可以呈現、收集一般無法查覺的刺激與反應
- 時間:以毫秒計
- 強度:接近閾限
- 使用儀器
- 早在十九世紀Wundt就設計了!
- 台大心理系所藏古典儀器
[編輯] Case Study 5
- 葉重新與劉英茂(1972)檢驗辨識漢字時可能影響的因素
- 測量漢字的辨識閾(recognition threshold)
- 實驗操弄漢字的意義度、筆劃及對稱性
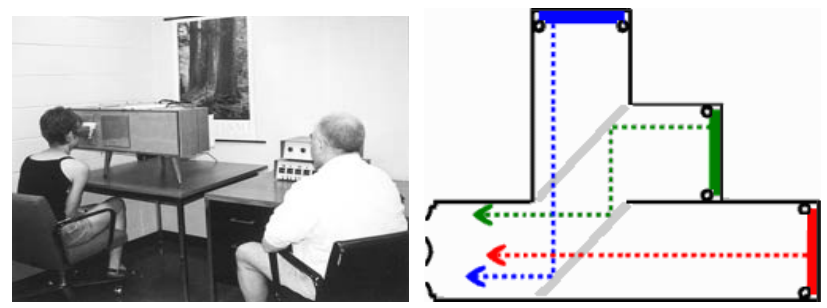
- 實驗利用吉氏速示器(Gerbrands tachistoscope)
- 程序:極限法(limit method)
- 結果:意義度愈高,筆畫愈少的漢字辨識閾愈低
- 速示器(tachistoscope)
- 快速呈現刺激
[編輯] PC與Psychology
- 實驗控制上常用PC (personal computer)
- 快速呈現
- 隨機排列
- 收集資料
- .....
[編輯] 心理學實驗中另一項問題
- Demand characteristics
- 實驗參與者會揣測主試者的意圖,而試著去符合或不符合主試者的要求,造成反應偏誤,不該顯著的結果卻顯著。
- 情境
- 防音暗室
- 一堆怪機器(自己拉的線、用角鋼....)
- 面貌凶惡的男主試
- 大一修普心嫩嫩的實驗參與者
- 主試問:「有沒有看到!」
[編輯] Two meanings of control
- Control of IV
- Spallazani實驗中精液的不同
- Control environment
- 實驗組與控制組間的差異除了上面控制以外控制成相當